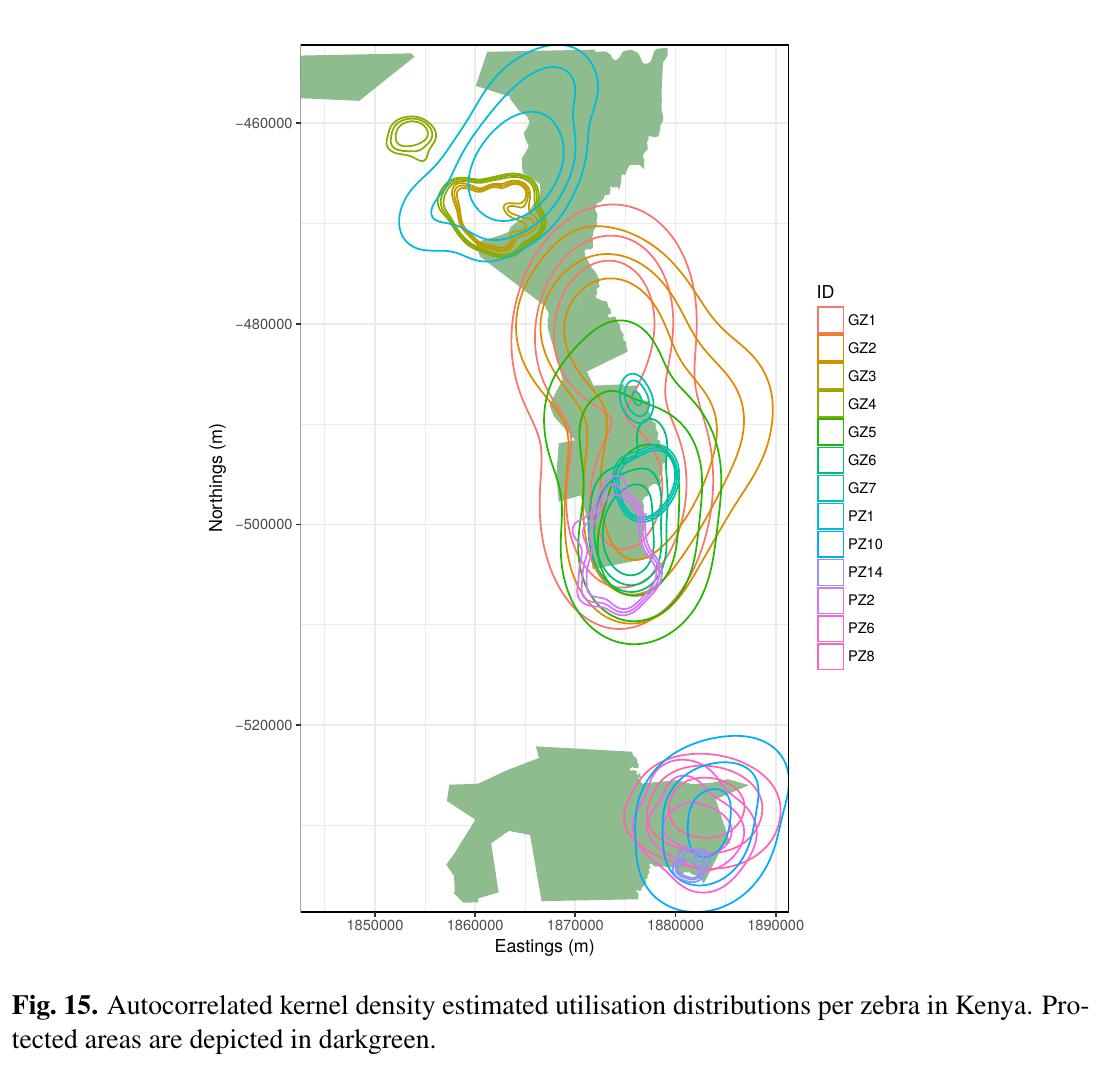
The M.Sc. thesis “Can animal movement and remote sensing data help to improve conservation efforts?” by Matthias Biber M.Sc. student within the Global Change Ecology program handed in his thesis. He explored the potential of remote sensing data to explain animal movement patterns and if these linkages can help to improve conservation efforts. He used Zebra as study animal in Southern and Eastern Africa. The first supervisor was Martin Wegmann, the second supervisor of his M.Sc. was Thomas Müller from BIK-F.
The M.Sc. thesis “Can animal movement and remote sensing data help to improve conservation efforts?” by Matthias Biber M.Sc. student within the Global Change Ecology program handed in his thesis. He explored the potential of remote sensing data to explain animal movement patterns and if these linkages can help to improve conservation efforts. He used Zebra as study animal in Southern and Eastern Africa. The first supervisor was Martin Wegmann, the second supervisor of his M.Sc. was Thomas Müller from BIK-F.
abstract:
Climate and land-use change have a growing influence on the world’s ecosystems, in particular in Africa, and increasingly threaten wildlife. The resulting habitat loss and fragmentation can impede animal movement, which is especially true for migratory species. Ungulate migration has declined in recent years, but its drivers are still unclear. Animal movement and remote sensing data was combined to analyse the influence of various vegetation and water indices on the habitat selection of migratory plains zebras in Botswana’s Ngamiland. The study area experienced a more or less steady state in normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI) over the last 33 years. More than half of the study area was covered by PAs. NDVI increased stronger in PAs compared to areas that were not protected. NDVI was always higher in the Okavango Delta compared to the Makgadikgadi Pans. Although zebras are thought to select for areas with high NDVI, they experienced a lower NDVI in the Makgadikgadi grasslands during wet season. Step selection functions (SSFs) showed that NDVI derived from Landsat as well as NDVI derived from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) were significant drivers of habitat selection across all individuals. Migration seems to be driven by the high nutritional value of the Makgadikgadi grasslands and not seasonal resource limitation. Landsat imagery was shown to provide different environmental information compared to MODIS data. This highlights not only the importance of NDVI for explaining animal movement, but also the importance of Landsat imagery for monitoring habitat extent and fragmentation. Incorporating the animal’s behavioural state and memory into SSFs will help to improve our ecological understanding of animal movement in the future.