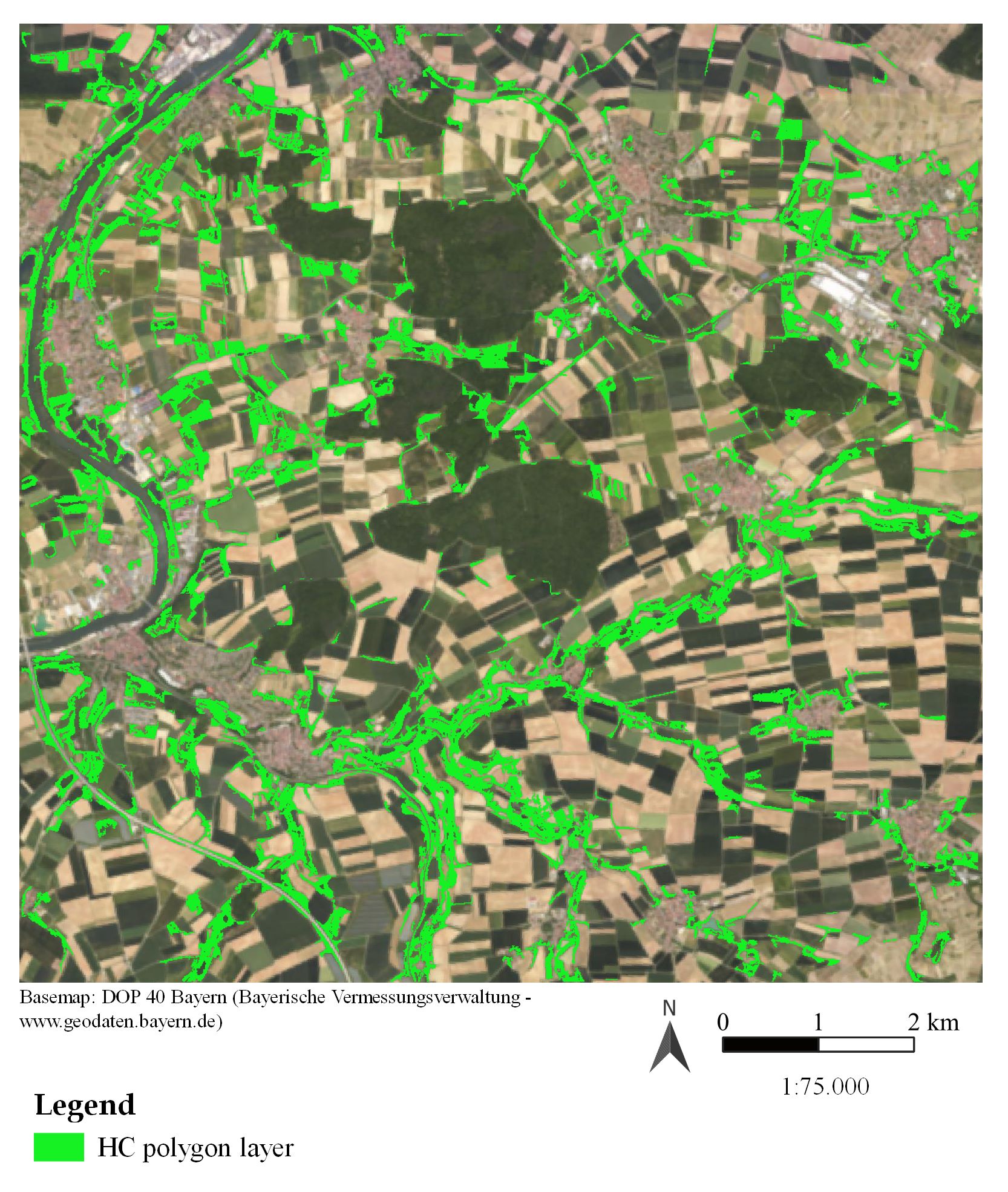
From the abstract: Hedgerows play a crucial role in agricultural landscapes by supporting biodiversity, preventing soil erosion, and enhancing ecosystem services such as water regulation and climate mitigation. However, agricultural intensification has led to significant losses of these features, threatening environmental health and biodiversity. This thesis explores the potential of remote sensing data for detecting hedgerows and copses in Lower Franconia. Using a pixel-based classification method with multi-temporal Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data, the research aims to create a polygon layer representing Small Woody Features. Key questions include evaluating the suitability of open-source, medium-resolution satellite data for detecting hedgerows and copses, identifying the most meaningful features for classification accuracy, and comparing the results to very high-resolution datasets such as the DOP Bayern imagery and the Copernicus Small Woody Features layer.
1st supervisor: Prof. Dr. Tobias Ullmann
2nd supervisor: Sebastian Buchelt