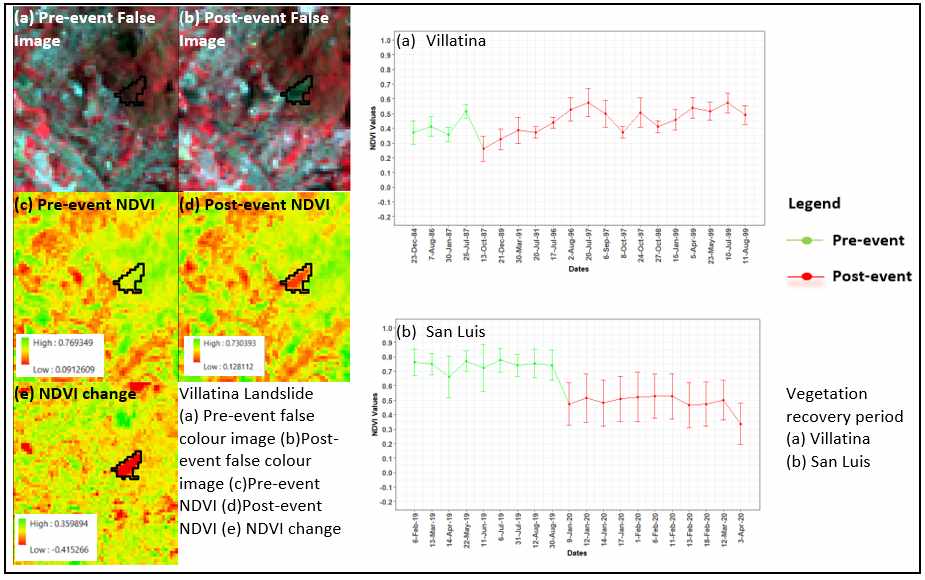
Segun will defend his M.Sc. “Application of Remote Sensing Techniques to detect historical landslides for improving risk assessment in Antioquia, Colombia.” on Oct. 16th at 10 am. From the abstract:
“In developing countries, current urbanization trends are leading to the development of settlements in endangered areas. Due to the lack of space and favourable land prices, occupation takes place mainly on cities’ edges, which are often characterized by steep slopes and are therefore areas prone to landslides. This triggers an increase of both the exposure to risk and the vulnerability of the inhabitants. Moreover, anthropogenic drivers such as the removal of vegetation, as well as the increase of heavy rainfall events due to climate change contribute greatly to subsequent occurrence of landslide risk. Landslides are a common hazard in the Antioquia region in Colombia and the number of people living in vulnerable areas is high. Assessing this risk involves acquiring information about environmental and triggering factors, historic landslide events (information about past events) and extent of damage caused. Hence, the detailed information about past events, which is often non-existent or incomplete, is necessary. In this context, the objective of this study is to combine sources of information, such as non-spatial databases, the media and Earth Observation data to localize historical landslide events in Antioquia, Colombia, with the ultimate aim of creating a rare landslide geodatabase based on remote sensing techniques. As a result, 25 landslides were identified by means of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA), using Landsat and Sentinel-2 imagery. Afterwards, two applications were conducted. First, landslides and the vegetation recovery period were analysed based on the NDVI values, showing a gradual recovery process at each location after the landslides. Second, the link between topographic factors and landslides in the region is explored. Overall, this work uses remote sensing techniques, to detect landslides locations independently of their various causal factors, determine the exact location that is missing in other inventories, status of the location before and after the event and also vegetation growth of each location by considering the index.