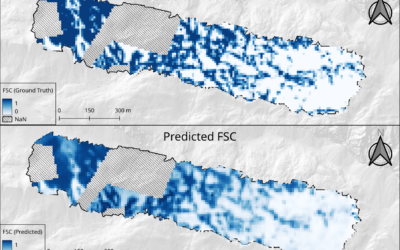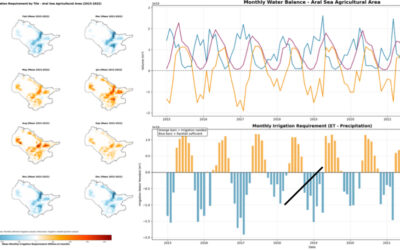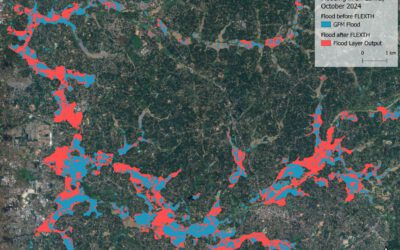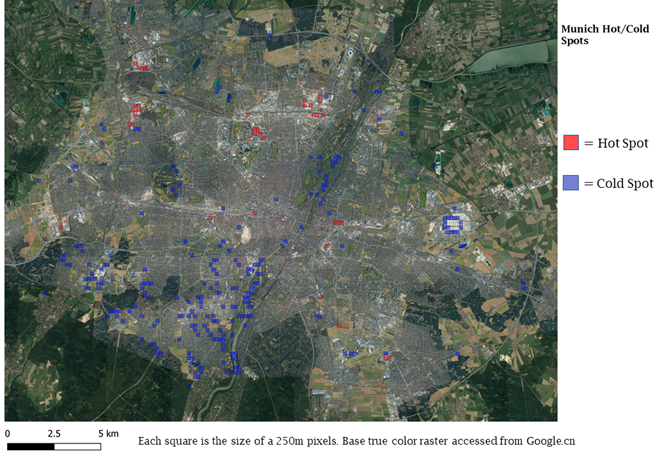
Michael Wang will present his thesis “Comparison of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using the World Settlement Footprint Imperviousness Layer” on Sept. 17th at 10am. From the abstract: “In the growing field of surface urban heat island (SUHI) analysis, impervious surface area (ISA) has been shown to have a strong relationship with land surface temperatures (LST) in cities. Using a globally available high-resolution imperviousness data set, the SUHI intensities (SUHII) of 18 cities of various regions and climates have been derived using three different imperviousness related metrics. The distance to the weighted center of the city provides the most intuitive quantification, however, it is least statically robust, unlike using ISA directly, whose lack of intuitive spatiality must be made up for in other ways. The distance to perviousness offers a compromise between the two, although its synthesis is completely idiosyncratic to its city due to differing urban landscapes. By decomposing the distance intensity into the pervious and impervious components, cities can be categorized into four groups based on combination of cooling and heating effects of each. Further, the ISA intensities can be categorized more broadly as those driven by the urban fabric vs by the industrial zone. Over all the cities, summer dryness is associated with lower or even negative SUHII.”

![FW: [EORC Talk] Pathways towards a Healthy City – 10 March 2026, 03 pm](https://eagle-science.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/image001.jpg)