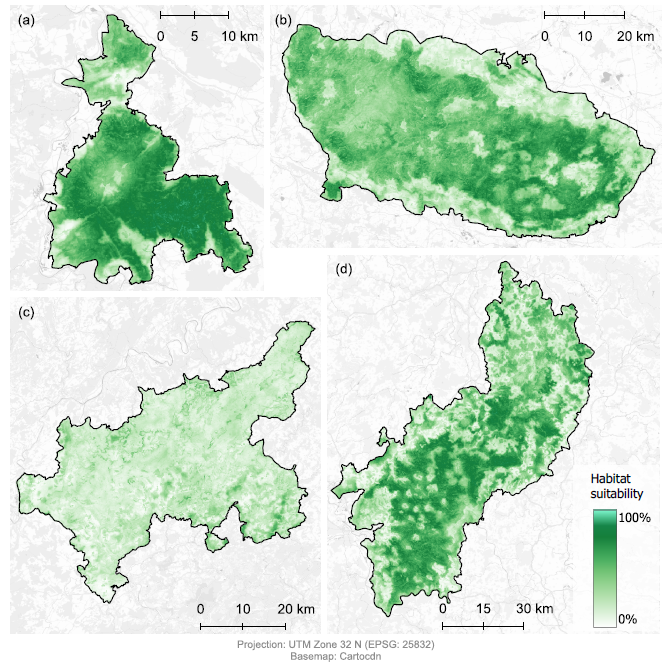
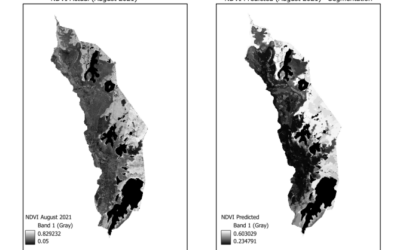
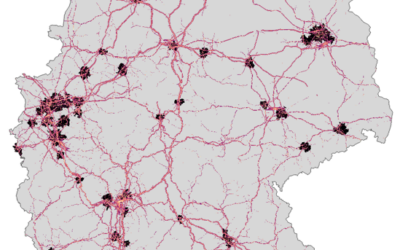
From the abstract: Forests provide essential benefits to human well-being, referred to as Nature’s Contributions to People (NCP), including carbon storage, water filtration, biodiversity, and recreation. However, increasing human activities and landuse changes have degraded wildlife habitats, threatening biodiversity and reducing NCP. This study explores the synergies and trade-offs between the conservation of the European wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris), an umbrella species promoting large and connected forest habitats, and the supply of forest-related NCP in German protected forests. Key factors influencing wildcat habitats are identified and their overlap with four selected NCP, namely carbon sequestration, water retention, timber potential, and recreational value, is examined. The analysis integrates remote sensing methodologies, including species distribution modelling and the InVEST water yield model, with statistical analysis, including correlations, spatial congruence, and k-means clustering, to assess synergies and trade-offs.
1st Supervisor: Dr. Michael Thiel 2nd Supervisor: Dr. Janina Kleemann (Martin-Luther University Halle-Wittenberg)