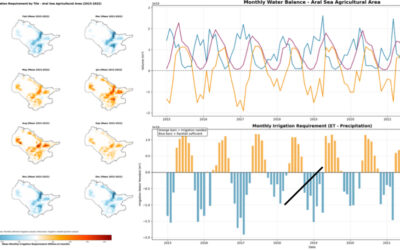
Actual evapotranspiration (ETact) is an essential component of the water balance and its determination for large areas is difficult on regional scale and can be explored within an innovation laboratory. The use of remote sensing data to determine ETact is particularly suitable to provide area based indicators for the evaluation of the efficiency and productivity of irrigation systems. Seasonal analysis of ETact is hampered by either spatial (MODIS) or temporal (Landsat) resolution. In order to provide a high-resolution (temporal and spatial) and dense remote sensing dataset Landsat and MODIS data will be fussed using the ESTARFM algorithm.
(ETact) is an essential component of the water balance and its determination for large areas is difficult on regional scale and can be explored within an innovation laboratory. The use of remote sensing data to determine ETact is particularly suitable to provide area based indicators for the evaluation of the efficiency and productivity of irrigation systems. Seasonal analysis of ETact is hampered by either spatial (MODIS) or temporal (Landsat) resolution. In order to provide a high-resolution (temporal and spatial) and dense remote sensing dataset Landsat and MODIS data will be fussed using the ESTARFM algorithm.
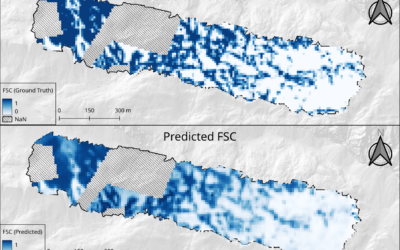
EAGLE Innolab Presentation: “From UAV to Satellite: Fractional Snow Cover Estimation at Sentinel-2 Resolution”
On March 03, 2026, Lutz Kleemann will present his Innolab results on "From UAV to Satellite: Fractional Snow Cover Estimation at Sentinel-2 Resolution" at 12:00 in seminar room 3, John-Skilton-Str. 4a. From the abstract: Fractional Snow Cover (FSC) estimation is an...