The MSc thesis by Asja Bernd titled “Mind the Gap: A Global Analysis of Grassland Fragmentation using MODIS Land Cover Data” is handed in. Very interesting results on global grassland fragmentation. Read the abstract:Around the world, grassland and savannah ecosystems are under intense anthropogenic use, yet research has not given them much attention. One significant threat is fragmentation, reducing habitat connectivity and hindering species dispersal. Using MODIS land cover data from 2012, combined with infrastructure data derived from VMAP0 and OpenStreetMap, I assessed the fragmentation of grasslands on a global scale. The metrics applied were patch size, distance to the euclidean nearest neighbour and number of neighbours per patch. To quantify the contribution of human pressure to fragmentation, the results were correlated with the Human Influence Index and human population density. For subsets, selected from the Global 200 Ecoregions, I analysed land cover data from 2001 and 2012 to determine
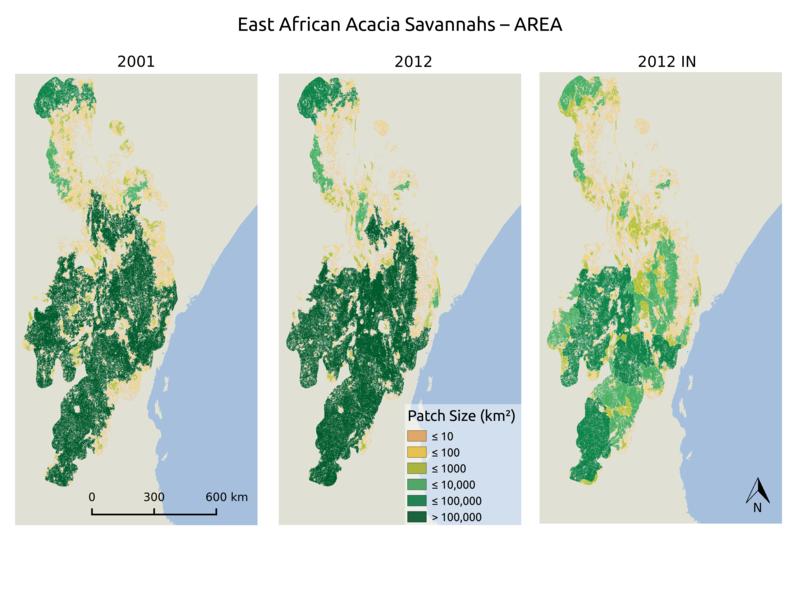
The MSc thesis by Asja Bernd titled “Mind the Gap: A Global Analysis of Grassland Fragmentation using MODIS Land Cover Data” is handed in. Very interesting results on global grassland fragmentation. Read the abstract:Around the world, grassland and savannah ecosystems are under intense anthropogenic use, yet research has not given them much attention. One significant threat is fragmentation, reducing habitat connectivity and hindering species dispersal. Using MODIS land cover data from 2012, combined with infrastructure data derived from VMAP0 and OpenStreetMap, I assessed the fragmentation of grasslands on a global scale. The metrics applied were patch size, distance to the euclidean nearest neighbour and number of neighbours per patch. To quantify the contribution of human pressure to fragmentation, the results were correlated with the Human Influence Index and human population density. For subsets, selected from the Global 200 Ecoregions, I analysed land cover data from 2001 and 2012 to determinetrends over time. Globally, grasslands are highly fragmented by infrastructure, which reduced patch size by more than 50 %, and significantly increased isolation. Human pressure seems to act as a driver of fragmentation, diminishing patch size and the number of neighbours, while increasing the distance to neighbours. For the subsets, results varied, but two of three metrics indicated an increase in fragmentation between 2001 and 2012. In the face of declining migrations of terrestrial mammals and increasing human pressure, a better understanding of the effects of fragmentation is needed to develop adequate management and protection strategies.Supervisor: Neil Burgess (UNEP) and Martin Wegmann